2022 / 01 / 26
Unlike Spot and Projection welding which are static welding processes, seam welding is accomplished through motion. A seam welding machine has one or two motor-driven wheels rotate to create a series of overlapping spot welds on sheet components to achieve air and/or liquid proof sealing on the welded part. The current passes through these rollers and the components to be welded are pressed in between them. The electrical resistance within the electrode rollers generates heat that joins the weld materials continuously.
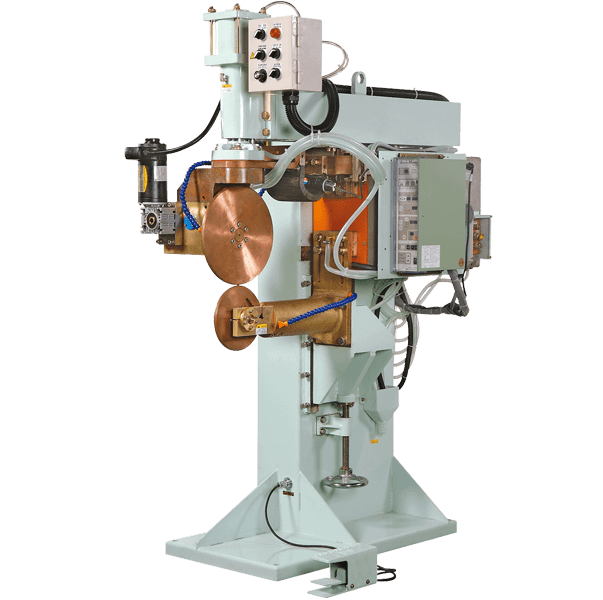
Universal Seam Welder with roller electrodes
We can further distinguish seam welding (overlapping and continuous) and the so-called roll spot welding. Seam welding separates into continuous seam and pulse seam. The continuous seam is an overlap of spot welds without cool time while pulse seam is an overlap of spot welds with cool time but so short that the spots are still connected together. Both continuous seam and pulse seam sometimes can run on the same machine. The selection between continuous seam and pulse seam can be decided based on the sheet component material and the weld appearance.
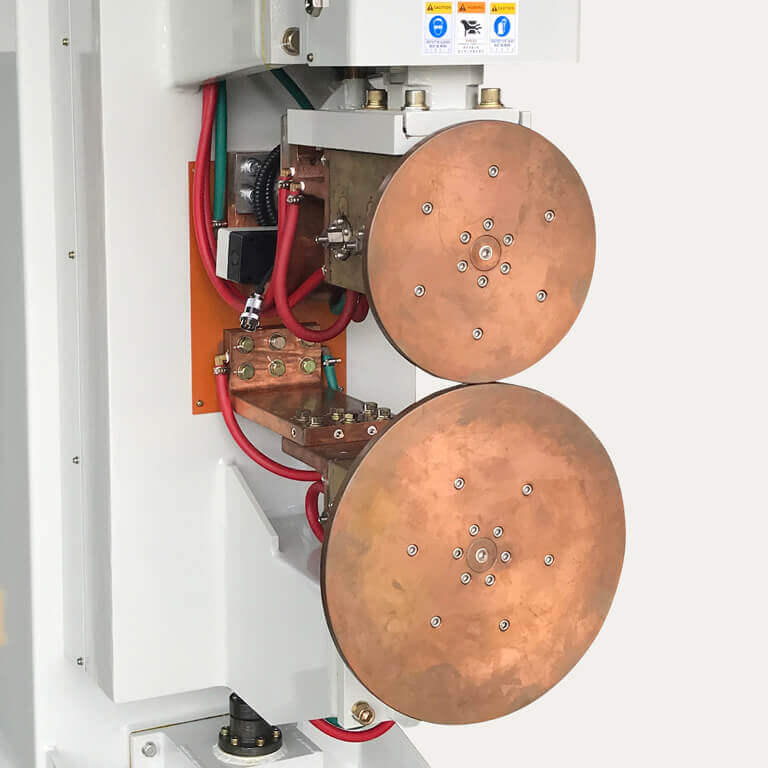

Roller Electrodes Close-Up
Roll spot welding is an interchange between a series of spot welds and a period of cool time but without opening the electrode during the welding process. Roll spot is well depicted in the brake shoe seam welding process where the embossments on the rim are roll spot welded. Another crucial feature of the resistance seam welding machine is the welding rod or electrode. It is driven by a wheel that itself is motor-driven. That wheel is opposite to the driving force of the fixed rod. This setup can be used for non-hermetic seam welding (rolling resistance welding) and is very suitable for joining metal plates.
Now, let us take a closer look at the different techniques.
In this type of welding, when the wheel moves along the workpiece, current pulses are intermittently provided. These intermittent current pulses and the pressure provided by the wheels form individual spot welds, and these spot welds are not sealed joints. Also, this batch method allows the workpiece to automatically move from one welding position to another welding position. It is particularly suitable for materials made of thicker sheets and resistant to continuous movement methods.
The frequency at which current is supplied applied to the workpiece is the primary factor when it comes to seam welding power supplies and control. The weld can be continuous, overlapping (intermittent), or a roll spot weld, depending on the frequency and speed.
Continuous Seam welds are commonly utilized to create continuous gas- or water-tight seams in sheet components such as automotive gasoline tanks. The method is also used to weld longitudinal weld joints in structural tubular sections where leak-tight seams are not required. Most common are two-wheel electrodes, or one translating wheel and one stationary mandrel setups that supply the current and pressure.
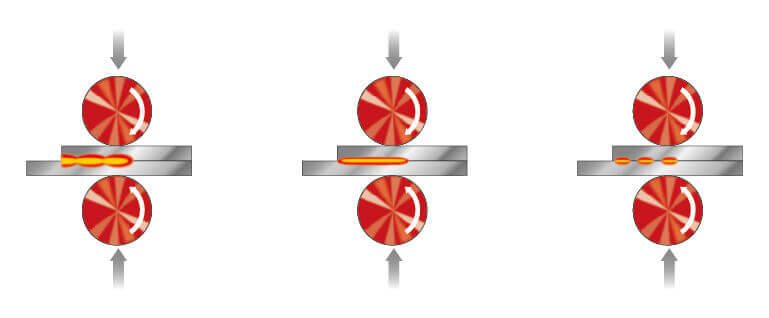
Comparison of Intermittent, Continuous and Roll Spot Welding
Seam welders Internal and External cooling on the electrode wheels. The heat generated during the seam welding process can be very large. Therefore, seam welders usually use a water cooling process to cool the electrodes (wheels), controller components, and transformers. The selection between The cooling system varies depending on the sheet component material, desired weld strength , and applications of the weld part.
Considering that welding is carried out under extremely high temperature and applied pressure, the final result of seam welder operation must be very durable. If you do it right, the result will be much stronger than the material that forms the weld. In the past, seam welding equipment has been used to make steel beverage cans. However, currently, seam welding is used to manufacture rectangular or round steel pipes. Another notable feature of the seam welding machine is that its welding rod is driven by a wheel driven by a motor, which is opposite to the driving force of the fixed rod. This mechanism produces non-hermetic seams (rolling resistance welding), and it is highly suitable for joining metal plates.
The advantage of the seam welder is that it can form a clear weld without the formation of gas or welding vapors. There is also no need to use filler contact material. The connecting material can be airtight and liquid impermeable and can be used in a variety of applications. For many products, this impermeable seam is vital. In addition, it is possible to achieve faster cycle times compared to spot welding.
The process can be fully automated, making it a highly repeatable process. Besides, seam welding machines can produce single and parallel seam welding at the same time, which increases the production efficiency. Also, the overlapping area can be more finely adjusted compared to spot or projection welds. Seam welding is especially efficient for sheet metal fabrication because it can result in weld joints that are stronger and more durable than the material of the metal sheets itself.
But there are also some drawbacks. While resistance seam welding can well form a straight line link, the roller cannot create more complex curved welds. Welding is also not possible at internal corners or where other component features prevent the wheel electrodes from entering. This process is also not suitable for joining metal plates with a thickness of more than three mm. Due to the speed of the rollers, skilled operators may be required to ensure welding quality, and welding machinery is also expensive.
One primary swam welding application lies in the assembly of fuel tanks since it is adept at welding liquid-tight parts. The seam welders are also used to weld vessel parts that need to be completely watertight or airtight. Although other types of welding processes are also capable of creating airtight and watertight seals, not more so than seam welding as they are sometimes not able to ensure clean welds. And seam welding on the other hand can achieve both. It is also frequently used for all kinds of barrels as well as exhaust system components, aircraft tanks, refrigerators, oil transformers, and so on,

Seam Welded Water Tanks
Another common application of seam welders is the welding of pipes and tubes. This is because resistance seam welding can be undertaken in the relevant field without having to use any fusional metals in the process. Therefore, the pipes and tubes will not turn out unsightly because there are no weld beads that may ruin the aesthetics. The welding techniques used in the pipes and tubes field can produce seamless joints which you can barely feel at the joining surface. The most common materials used for seam welding include stainless steel, nickel, and magnesium alloys.
As a Dahching customer, you will benefit from our welding expertise, no matter which type of welding machine you are looking for. Our machines have a variety of automation features, such as flexible clamping. If you are looking for a total solution we can also assist you with planning a whole welding equipment production line to create the perfect combination of robotic technology, seam welding machines including the gun, fixtures, rollers, etc. Each customer of ours gets the individual solution they deserve. As a starting point, first choose the type of Seam welding machine most suitable for your application: transversal (also called circular seam welders), longitudinal or universal for maximum flexibility.
Just click on the machine type you are most interested in to learn more about it.
If you are more interested in Flash Butt Welding Machines Just click here.
How can we help?
If you have any business inquiries or product questions,
please feel free to contact us.